One of the more difficult aspects to understand about design control regulation is how all of the design control elements should work together. The design control process is anything but linear. The interrelationships between design control elements is not complex, but there are many interactions that must be understood for device manufacturers to effectively execute a design control process. The FDA does not directly explain these relationships in the regulation, guidance or preamble but nevertheless expects them to be correctly implemented.
The following figure and referenced table is a graphical representation of the interfaces between all design control elements. Each tie between the design control elements is labeled with a relationship ID#.
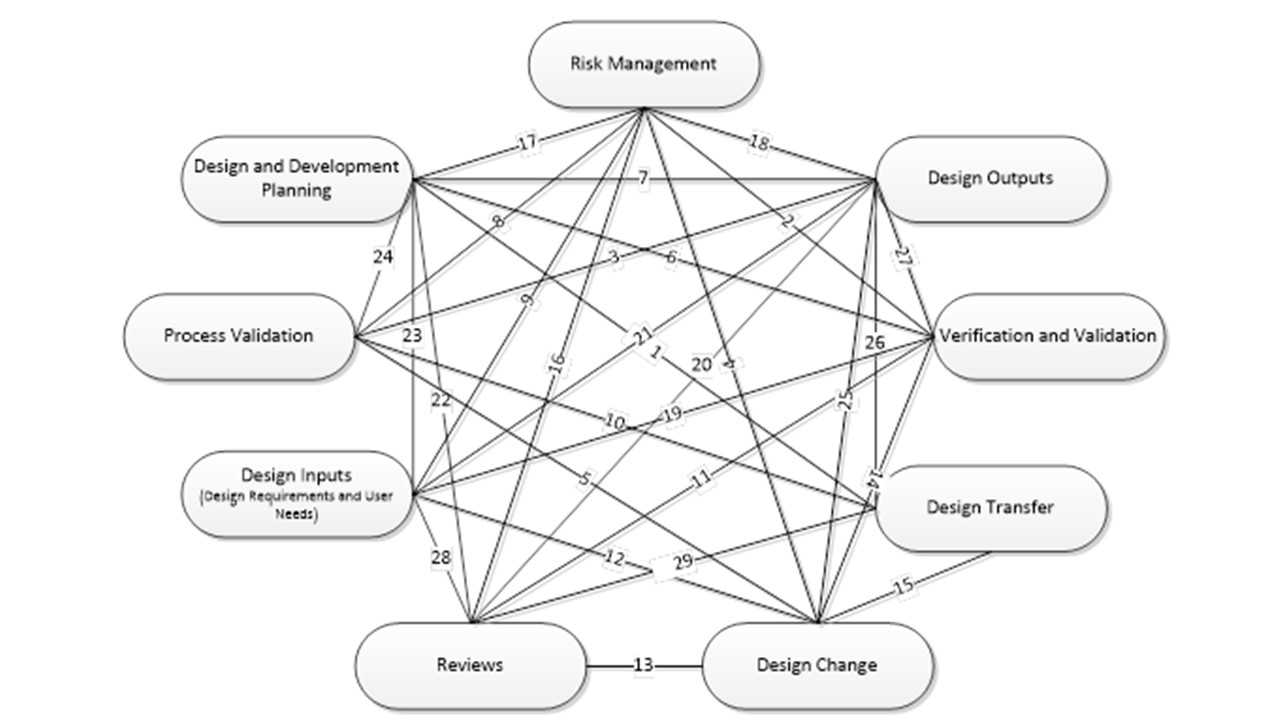
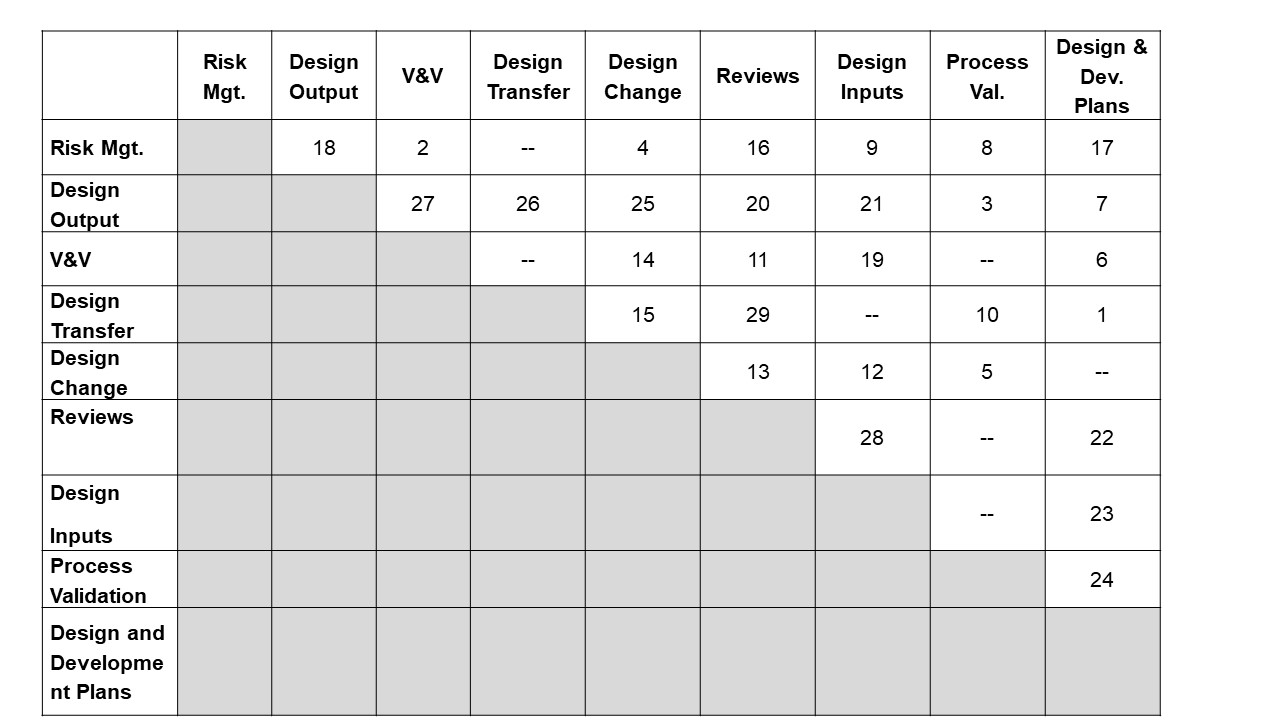
1 | Design Transfer | The design and development plan should specify timing and responsibility of design transfer activities such as design transfer reviews, completion of process validation, completion of production inspection specifications, DHR forms, and manufacturing procedures, etc. The design and development plan should also specify timing of design transfer phases (as applicable). It is best practice to reference the design transfer checklist document # in the design and development plan as design transfer is occurring and as the design and development plan is updated. |
| Design & Development Plan | ||
2 | Risk Management | The risk assessment is typically used to refine acceptance criteria in verification and validation protocols and to influence verification/validation methods. Even though the design input requirements will drive the acceptance criteria, the risk assessment will influence such things as the required confidence level and method of verification or validation. For lower risk design features or performance requirements, lower confidence levels may be acceptable. It may also be acceptable to perform verification by inspection or by analysis for lower risk features, where this may not be the case for higher risk features which would typically drive verification by testing. In some instances when a risk assessment is performed on a manual process or assesses variability of a user during human factors studies, it may be appropriate to use the results of verification or validation to lower the original probability of occurrence of harm. This may be justified in some instances if the original identified probability of occurrence of harm is based on team member subjective input and not on objective data. If the verification or validation was performed by hundreds or thousands of manual users which repeat the same operation, risk assessment reviewers may be inclined to use this data to justify reducing the probability of occurrence. If this approach is justified, the verification/validation report should be referenced as a risk control method (even though technically it is not a control). |
| Verification and Validation | ||
| 3 | Design Output | The design outputs from the design process (i.e. drawings) which define the device are used to guide process validation acceptance criteria. The design outputs will specify critical features and inspection criteria which will be translated into manufacturing product acceptance criteria. The manufacturing acceptance criteria will be used to drive acceptance criteria in the process validation (Process Performance Qualification and Product Performance Qualification). |
| Process Validation | ||
| 4 | Risk Management | Every time a design change is proposed, a risk assessment should be performed (or an existing risk assessment should be reviewed) to determine if the design change will impact/alter the current risk levels. |
| Design Change | ||
| 5 | Design Change | Every time a design change is proposed, the impact to the design outputs should be assessed to determine if the change will invalidate the process validation associated with those design outputs. (e.g. did a critical feature or acceptance criteria on the design output change which would require re-validation of the process which makes the device) |
| Process Validation | ||
| 6 | Verification & Validation | The design and development plan should specify timing and responsibility of verification and validation activities such as protocol development, execution and report generation. It is best practice to reference the verification and validation protocol and reports document #’s in the design and development plan when V & V is completed and when the design and development plan is updated. |
| Design and Dev. Plan | ||
| 7 | Design Output | The design and development plan should specify timing and responsibility of design output activities such as software code, component drawings, electrical schematics, manufacturing procedures, inspection requirements, etc. It is best practice to reference the design output document #’s (usually high level) in the design and development plan as design outputs are being created and when the design and development plan is updated. |
| Design and Dev. Plan | ||
| 8 | Risk Management | A design risk assessment will identify device hazards which may lead to patient harm. These hazards will be used as inputs into the process risk assessment for a device manufacturing process. (The hazards in the process risk assessment should contain a reference back to where they were initially identified in the design risk assessment.) The process risk assessment will evaluate what process steps may lead to these hazards occurring. Those process steps which have a high probability of causing these hazards (higher risk) should be given additional process development and validation scrutiny. As an example, if a manufacturing process generates a device feature which is critical to the safety of the device, that process step should have higher process capability requirements (1.33 Cpk vs. 2.00 Cpk) than other features which are not as high risk. |
| Process Validation | ||
| 9 | Risk Management | Typically design risk assessments and design inputs should be developed simultaneously. The initial version of the risk assessment will identify hazards and associated risks which may need to be mitigated. An ideal method of mitigating risk is to generate a design input requirement which will lead to generating an output that is intended to mitigate the risk (via design control). It is best practice to reference these requirements and the verification reports (evidence of verifying that the outputs meet the design inputs) in the “risk control” field of the risk assessment. This documentation practice provides objective evidence that the design control feature was implemented and verified. The residual risk evaluation should be performed with consideration of the completed verification which may in turn lead to a lower residual risk. For those identified risks which lead to creating design inputs, it is also best practice to reference the line item # (or ID#) from the risk assessment in the design input requirement line item to provide the source of the design input requirement (source = risk assessment). |
| Design Inputs | ||
| 10 | Design Transfer | Process validation for device manufacturing processes should be a required design transfer activity. Process validation should be specified as a requirement on the design transfer checklist. The process validation report(s) should be referenced in the design transfer checklist to provide objective evidence that process validation was completed. This also provides easy traceability during internal or external inspections. |
| Process Validation | ||
| 11 | Verification and Validation | Verification and validation protocols and reports should be reviewed prior to approval. Informal individual reviews are acceptable, a formal design review is not required. |
| Reviews | ||
| 12 | Design Change | Revisions to design input documents require changes to be approved through a formal change control process. When making design changes (i.e. to design outputs), an impact assessment should be performed to determine if the design inputs (or associated verifications and validations) are affected by the change. |
| Design Inputs | ||
| 13 | Design Change | Design changes should be reviewed prior to implementing the design change. Reviews can be individual or formal team design reviews (meetings). |
| Reviews | ||
| 14 | Verification and Validation | When making design changes (changes to design inputs or outputs), a verification and validation assessment should be performed to determine if the design change affects the validity of a previously performed verification or validation. If the validity of the verification or validation is in question, additional verification or validation may be required. |
| Design Change | ||
| 15 | Design Transfer | When making design changes (changes to design inputs or outputs), an impact assessment should be performed to determine if the design change affects the production specifications that were created during design transfer. |
| Design Change | ||
| 16 | Risk Management | Risk assessments and risk management reports should be reviewed prior to approval. |
| Reviews | ||
| 17 | Risk Management | The design and development plan should specify timing and responsibility of risk management activities/deliverables such as a risk analysis, risk management plan and report. It is best practice to reference the risk management plan and report document # in the design and development plan. |
| Design and Development Plan | ||
| 18 | Risk Management | During the risk analysis process, design outputs are reviewed to identify hazards that may be associated with the output. As a result of the initial risk analysis and evaluation, risk mitigation may be required. Design controls to mitigate risk are implemented by modifying or creating design outputs. |
| Design Output | ||
| 19 | Verification and Validation | Verification and Validation protocols should contain acceptance criteria which should be derived from the design inputs. The protocol should also include a trace matrix to tie the verification or validation test case to the input that is being verified/validated. |
| Design Inputs | ||
| 20 | Design Outputs | Design outputs should be reviewed prior to approval and release. Individual review of outputs are acceptable, formal design reviews are not required. |
| Reviews | ||
| 21 | Design Outputs | Design inputs guide the development of the design outputs during the design process. Design verification is performed to show that design outputs meet design inputs. A traceability matrix is used to tie design outputs back to design inputs. See traceability section in verification chapter for more details. |
| Design Inputs | ||
| 22 | Reviews | The design and development plan should specify when design reviews will be held, who is responsible for leading the reviews and what type of reviews will be held. It is best practice to reference the design review meeting minute’s document # in the design and development plan as design reviews are executed. |
| Design and Development Plan | ||
| 23 | Design Inputs | The design and development plan should specify what type of inputs will be developed, when the inputs should be completed, and who will be responsible for developing the inputs. |
| Design and Development Plan | ||
| 24 | Process Validation | The design and development plan should specify when process validation will be held and who is responsible for leading process validation activities (i.e. protocol development). |
| Design and Development Plan | ||
| 25 | Design Output | A change control process is required for all design changes (changes to design inputs or design outputs). As part of the change control process, an impact assessment should be performed to determine what outputs are affected by the change. It is best practice to include the change control reference number in the revision record of the output to tie the output revision to the change control record. |
| Design Change | ||
| 26 | Design Output | During the design transfer process, production specifications (design outputs) will be developed to support the production process. Also, design outputs which document the device design (i.e. device drawings) will be used to develop the production specifications during design transfer (also design outputs). |
| Design Transfer | ||
| 27 | Design Output | Design verification is performed to show that design outputs meet design inputs. Verification/Validation protocols should reference the design output document(s) # that are being used during verification or validation. |
| Verification and Validation | ||
| 28 | Reviews | Design inputs should be reviewed in a formal design review(s). If a design input requirement is developed or modified in a review, the document # of the meeting minutes from the review should be referenced in the design input requirement as the source of that requirement (traceability). |
| Design Inputs | ||
| 29 | Design Transfer | It is best practice to hold a formal design transfer review to ensure that all design transfer activities and deliverables have been completed. |
| Reviews |